A Patient Has Microcytic Hypochromic Anemia Which of the Following
A 15-year-old Lebanese boy was sent to the laboratory for an evaluation of anemia and had the following lab results. Folic acid deficiency anemia b.
A B C Causes of microcytic hypochromic anemia are decreased erythrocyte life span failure of mechanisms of compensatory erythropoiesis or disturbance of the iron cycle.

. Microcytic normochromic emacrocytic normochromic 2. Hypochromic microcytic anemia MLPA GTR Test ID Help Each Test is a specific orderable test from a particular laboratory and is assigned a unique GTR accession number. Here we report two.
Which of the following would be a plausible diagnosis for this patient. Iron deficiency anemia A peripheral smear shows a decreased RBC count with microcytic hypochromic cells with small grape-like inclusions in the RBCs on both Wright stain and Prussian blue stain. Microcytic hypochromic anemia can be caused by multiple reasons.
The format is GTR000000011 with a leading prefix GTR followed by 8 digits a period then 1 or more digits representing the version. Increased basal metabolic rate e. The physician suspects iron deficiency anemia.
Iron deficiency anemia is caused by defective heme synthesis. Reduced expression of adhesion molecules on endothelial cells. A child presents with microcytic hypochromic anemia.
Further laboratory testing reveals a normal total serum iron and iron-binding capacity. Swelling in the tissues ANS. Iron deficiency anemia is caused by defective heme synthesis.
Hemoglobin testing is particularly indicated in the following situations 8 9. Increased basal metabolic rate e. Anemia of inflammation and chronic disease.
Iron deficiency anemia and thalassemia are both classified as microcytic hypochromic anemias. Whereas thalassemia is caused by decreased globin chain synthesis. You can get this mineral by eating meat fish beans leafy green vegetables and chicken.
Which of the following is the correct classification of his anemia. The physician suspects iron deficiency anemia. Iron deficiency anemia and thalassemia are both classified as microcytic hypochromic anemias.
A patient has microcytic hypochromic anemia. Decreased erythrocyte life span b. Vascular obliteration crises of unclear etiology in patients from areas in which HbS andor HbC is widespread.
Microcytic hypochromic anemia after iron deficiency has been ruled out. A urinary screen for porphyrins was positive. Decreased erythrocyte life span.
There are several types of microcytic anemia. Indeed in EPP patients was observed a two-third decrease in. Microcytic hypochromic anemia is common form anemia primarily caused by fall in iron level below normal acceptable level.
Decreased erythrocyte life span b. CBC- Microcytic hypochromic anemia. Problem 8 Easy Difficulty.
Further laboratory testing reveals a normal total serum iron and iron-binding capacity. However the zinc protoporphyrin level was very high. Folic acid deficiency anemia b.
Failure of mechanisms of compensatory erythropoiesis c. Each of these conditions makes it difficult for the body to produce healthy red blood cells. B Iron deficiency anemia and thalassemia are both classified as microcytic hypochromic anemias.
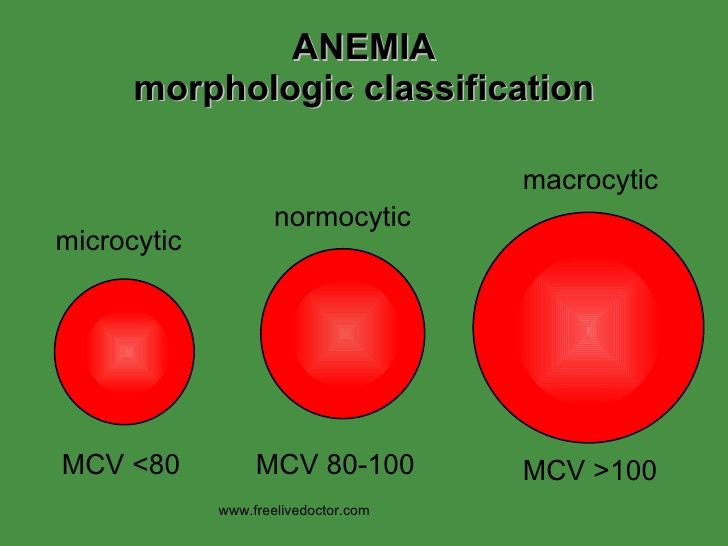
Microcytic anaemia is any of several types of anaemia characterized by small red blood cells called microcytesThe normal mean corpuscular volume abbreviated to MCV on full blood count results and also known as mean cell volume is approximately 80100 fLWhen the MCV is microcytic and when 100 fL macrocytic the latter. Decreased erythrocyte life span b. Which of the following is a microcytic hypochromic anemia.
Disturbances of the iron cycle d. WBC 75X109L RBC 59X1012L Hgb 116 gdL Hct 36 What is the presumptive clinical condition. A child presents with microcytic hypochromic anemia.
Swelling in the tissues. BM aspirate shows marked erythroid hyperplasia and. DMT1 has a vital role in iron homeostasis by mediating iron uptake in the intestine and kidneys and by recovering iron from recycling endosomes after transferrin endocytosis.
Disturbances of the iron cycle d. Failure of mechanisms of compensatory erythropoiesis c. Microcytic anemia can be caused by several different health conditions ranging from mild problems to more serious issues.
All of the following are symptoms of iron deficiency anemia except. It may be caused due to unhealthy lifestyle dietary deficiency or presence of other underlying systemic condition. Mutations in SLC11A2 cause an ultra-rare hypochromic microcytic anemia with iron overload AHMIO1 which has been described in eight patients so far.
Which of the following pathogenic mechanisms may cause anemia in this patient. Disturbances of the iron cycle. A 10-month-old boy presents with failure to thrive.
The most common types of microcytic anemia are. Which of the following was most likely the. The most common cause being iron deficiency.
Which of the following anemias can be categorized as microcytic-hypochromic. Select all that apply a. A urinary screen for porphyrins was positive.
Select all that apply a. Which of the following pathogenic mechanisms may cause anemia in this patient. Failure of mechanisms of compensatory erythropoiesis c.
59 A patient has microcytic hypochromic anemia. It is important to work with a healthcare team to find the underlying cause. Most of the Hb is HbF type.
However the zinc protoporphyrin level was very high. On the contrary mild hypochromic microcytic anemia has been reported in 33 of men and 48 of women with EPP Holme et al 2007 although the explanation of the why this occur remains unclear. Sideroblastic anemia all the above Microcytic HypochromicMicrocytic Normochromic Microcytic Hyperchromic Iron deficiency Anemia of inflammation and chronic diseaseHereditary spherocytosis.

Pin On Hematology Blood Cells Lymphadenopathy Anemia Leukemia

Accessmedicine View Large Medical Laboratory Science Student Medical Laboratory Scientist Medical Laboratory Science
















Comments
Post a Comment